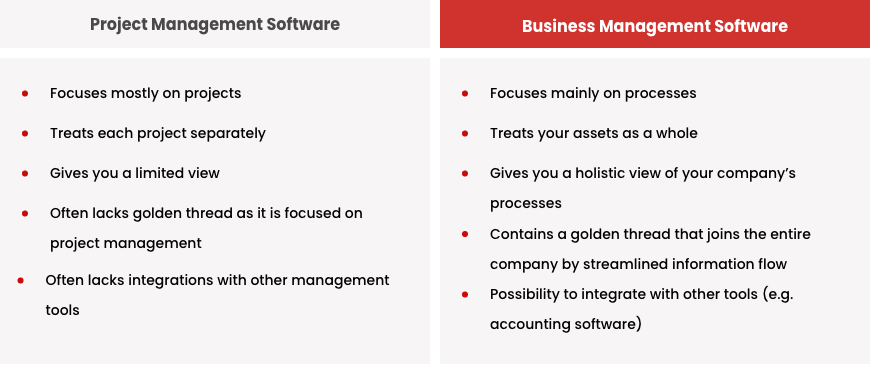
Project Management focuses on specific projects with defined goals and timelines. Business Management oversees the overall operations and long-term strategies of an organization.
Project Management involves planning, executing, and closing projects. Each project has clear objectives, deadlines, and resources. Business Management, on the other hand, handles the entire organization. It includes managing departments, setting long-term goals, and ensuring overall growth. Understanding both is crucial for organizational success.
Project Managers ensure projects meet deadlines and budgets. Business Managers focus on sustainable growth and efficiency. Both roles require leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills. Knowing the difference helps in assigning the right tasks to the right people. This ensures better outcomes and streamlined processes.
Credit: archdesk.com
Introduction To Management Disciplines
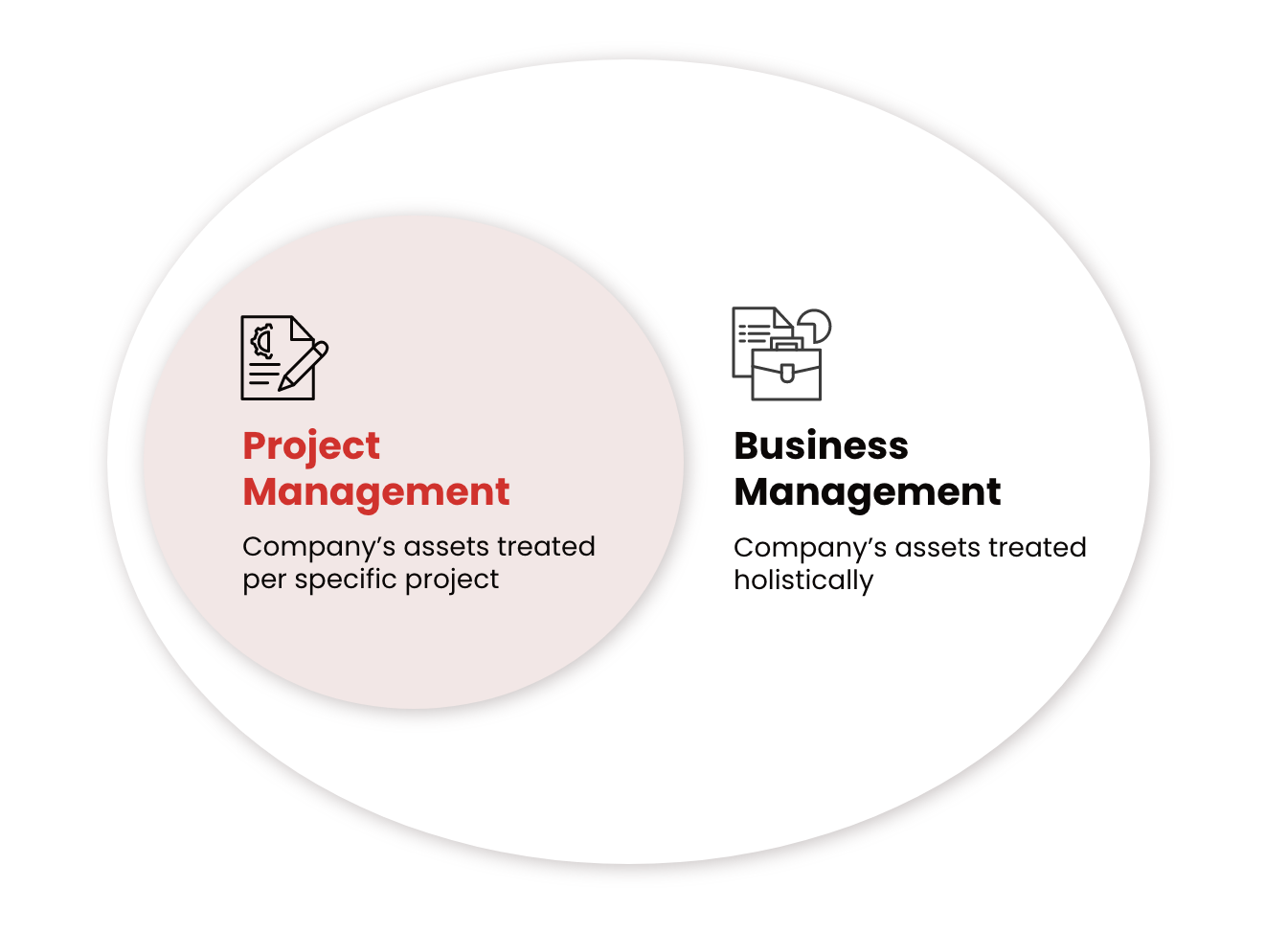
Management is essential for any organization. It ensures that goals are achieved. There are different types of management disciplines. Two of the main ones are Project Management and Business Management. Each has its own focus, methods, and goals. Understanding the differences helps in choosing the right approach.
Defining Project Management
Project Management is about handling specific projects. These are temporary and unique endeavors. The goal is to complete tasks within a set time frame. This discipline involves planning, executing, and closing projects. Key elements include:
- Scope: Defines what the project will achieve.
- Time: Specifies the project duration.
- Cost: Budgeting for the project.
- Quality: Ensuring the final deliverable meets standards.
- Resources: Allocating human and material resources.
- Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed.
Project managers use various tools and techniques. Examples include Gantt charts and Critical Path Method (CPM). These help in tracking progress and managing resources. Successful project management leads to the timely and within-budget completion of projects.
Defining Business Management
Business Management focuses on running a business efficiently. It is continuous and ongoing. The goal is to achieve long-term objectives. This discipline covers all aspects of a business. Key elements include:
- Strategy: Long-term planning for growth and success.
- Operations: Managing day-to-day activities.
- Finance: Budgeting and financial planning.
- Marketing: Promoting products and services.
- Human Resources: Hiring and managing employees.
- Customer Relations: Ensuring customer satisfaction.
Business managers need a broad set of skills. They must be good at problem-solving and decision-making. They also need to be effective communicators. Strong leadership is critical for business success. Business management ensures the organization runs smoothly and achieves its goals.
Core Objectives
The core objectives of project management and business management differ significantly. Understanding these differences helps in achieving the desired outcomes effectively.
Goals Of Project Management
Project management focuses on achieving specific goals within a defined timeframe. Here are the primary objectives:
- Delivering Projects on Time: Ensuring projects are completed by set deadlines.
- Staying Within Budget: Managing resources to avoid overspending.
- Meeting Quality Standards: Ensuring the final output meets the required standards.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Ensuring all stakeholders are happy with the project outcome.
Goals Of Business Management
Business management aims at the overall growth and stability of the organization. The main goals include:
- Increasing Profitability: Maximizing revenues while minimizing costs.
- Market Expansion: Exploring new markets and expanding the customer base.
- Enhancing Employee Performance: Improving productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Ensuring Sustainability: Implementing practices that ensure long-term business sustainability.
- Maintaining Competitive Advantage: Staying ahead of competitors through innovation and strategy.
Both disciplines require different approaches but are crucial for organizational success.
Key Responsibilities
Understanding the key responsibilities of project managers and business managers can help differentiate their roles. While both positions involve leadership and management, their focus areas and duties vary significantly. Let’s explore the specific responsibilities of each role.
Project Manager’s Role
A project manager oversees specific projects. Their main goal is to ensure the project is completed on time, within scope, and on budget. Here are some key responsibilities:
- Defining project scope and objectives
- Creating detailed project plans
- Allocating resources and setting deadlines
- Monitoring project progress
- Managing risks and issues
- Ensuring stakeholder satisfaction
- Reporting on project performance
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Scope Management | Defines project boundaries and deliverables |
| Resource Allocation | Assigns tasks and manages team resources |
| Risk Management | Identifies and mitigates project risks |
Business Manager’s Role
A business manager focuses on the overall health and growth of the business. Their responsibilities are broader and include strategic planning and operational management. Key responsibilities include:
- Setting business goals and objectives
- Developing strategic plans
- Managing overall operations
- Leading business development efforts
- Overseeing financial performance
- Ensuring customer satisfaction
- Building and maintaining relationships with stakeholders
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic Planning | Develops long-term business strategies |
| Operational Management | Oversees daily business activities |
| Financial Oversight | Monitors and manages financial health |
While both project managers and business managers play crucial roles, their responsibilities are distinct. Understanding these differences helps in appreciating their unique contributions to organizational success.
Skills And Competencies
Understanding the distinct skills and competencies for project managers and business managers is crucial. Both roles require unique abilities to thrive and achieve success. This section will delve into the specific skills needed for each role, helping to clarify their differences and importance.
Skills For Project Managers
Project managers need a diverse set of skills. These skills help them manage tasks and lead teams effectively. Key skills include:
- Leadership: Inspires and guides team members.
- Time Management: Plans and schedules tasks efficiently.
- Communication: Conveys ideas and updates clearly.
- Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates potential issues.
- Budget Management: Keeps project costs under control.
- Problem-Solving: Finds solutions to unexpected challenges.
- Technical Skills: Understands the tools and technologies used.
Skills For Business Managers
Business managers require a broader range of competencies. These skills enable them to oversee operations and drive growth. Key skills include:
- Strategic Planning: Sets long-term goals and strategies.
- Financial Acumen: Manages budgets and financial reports.
- Human Resource Management: Hires, trains, and motivates staff.
- Marketing Knowledge: Understands market trends and consumer behavior.
- Decision-Making: Makes informed choices for the business.
- Customer Relationship Management: Maintains strong client connections.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes and improves productivity.
Both roles share some common skills, yet they also require distinct competencies. Understanding these differences can help individuals excel in their respective fields. Each role demands a unique approach to leadership and management.
Methodologies And Approaches
Understanding methodologies and approaches is crucial in distinguishing between project management and business management. These methods shape how tasks are executed. They influence the overall success of the project or business.
Project Management Methods
Project management uses specific methods to manage tasks. Below are some key methods:
- Waterfall: Follows a linear approach. Each phase must be completed before moving to the next.
- Agile: Focuses on flexibility and customer feedback. Tasks are done in small, iterative cycles.
- Scrum: A subset of Agile. Uses sprints and roles like Scrum Master and Product Owner.
- Kanban: Visualizes tasks on a board. Helps in managing workflow and spotting bottlenecks.
- Lean: Emphasizes reducing waste and improving processes.
Business Management Strategies
Business management uses strategies to achieve goals. Here are some common strategies:
- SWOT Analysis: Identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Balanced Scorecard: Measures performance from financial, customer, internal processes, and learning perspectives.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzes competitive forces to understand market dynamics.
- BCG Matrix: Helps in portfolio management by categorizing products based on market growth and share.
- Value Chain Analysis: Examines internal activities to understand competitive advantage.
| Aspect | Project Management | Business Management |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Completing specific projects | Overall business success |
| Methods | Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Lean | SWOT, Balanced Scorecard, Porter’s Five Forces, BCG Matrix, Value Chain |
| Timeframe | Project duration | Long-term |
Tools And Technologies
Understanding the tools and technologies used in project management and business management is essential. Each discipline leverages specific tools to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and achieve goals. Here, we will explore the different tools used in both fields.
Project Management Tools
Project management tools help teams plan, execute, and track project progress. These tools are designed to support the various phases of a project.
- Gantt Charts: Visual timelines for project schedules.
- Kanban Boards: Visual workflow management.
- Project Management Software: Tools like Asana, Trello, and Jira.
- Time Tracking Tools: Track time spent on tasks. Examples: Harvest, Clockify.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitate team communication. Examples: Slack, Microsoft Teams.
Business Management Tools
Business management tools focus on broader organizational tasks. They assist in managing operations, finances, and human resources.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates core business processes. Examples: SAP, Oracle.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer interactions. Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot.
- Accounting Software: Manages financial transactions. Examples: QuickBooks, FreshBooks.
- Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS): Manages employee data. Examples: Workday, BambooHR.
- Business Intelligence Tools: Analyze data for informed decisions. Examples: Tableau, Power BI.
Both project and business management tools are vital. They help achieve efficiency and success in their respective domains.
Challenges And Solutions
Understanding the challenges and solutions in project management and business management is vital. Both fields have unique obstacles and require tailored strategies to overcome them. This section highlights these challenges and offers effective solutions.
Challenges In Project Management
Project managers face several challenges that can impact project success. These include:
- Scope Creep
- Budget Constraints
- Time Management
- Resource Allocation
- Risk Management
Scope Creep occurs when project requirements increase over time. To solve this, clearly define project scope and stick to it.
Budget Constraints can hinder project progress. To manage this, create a detailed budget plan and monitor expenses.
Time Management is crucial for meeting deadlines. Use project management tools to track progress and set realistic timelines.
Resource Allocation involves distributing resources efficiently. Ensure all team members have the tools and support they need.
Risk Management is about identifying and mitigating potential risks. Develop a risk management plan and prepare for unexpected issues.
Challenges In Business Management
Business management comes with its own set of challenges. These include:
- Employee Management
- Financial Management
- Market Competition
- Customer Satisfaction
- Regulatory Compliance
Employee Management involves keeping staff motivated and productive. Implement training programs and foster a positive work environment.
Financial Management requires careful planning and monitoring. Use financial software to keep track of income and expenses.
Market Competition can be intense. Stay ahead by innovating and understanding market trends.
Customer Satisfaction is key to business success. Focus on delivering quality products and excellent service.
Regulatory Compliance involves adhering to laws and regulations. Keep updated with legal requirements and ensure your business complies.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Scope Creep | Define and stick to project scope |
| Budget Constraints | Create detailed budget plan |
| Time Management | Use project management tools |
| Resource Allocation | Ensure proper tools and support |
| Risk Management | Develop risk management plan |
| Employee Management | Implement training programs |
| Financial Management | Use financial software |
| Market Competition | Innovate and understand trends |
| Customer Satisfaction | Deliver quality products |
| Regulatory Compliance | Keep updated with legal requirements |

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Career Pathways
Understanding the differences between project management and business management is essential for choosing the right career path. Each field offers unique opportunities and requires different skill sets. Let’s explore the career pathways in both domains.
Career Opportunities In Project Management
Project management careers focus on overseeing projects from start to finish. Professionals in this field ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
- Project Manager: Leads project teams and coordinates resources.
- Project Coordinator: Assists the project manager with administrative tasks.
- Project Scheduler: Develops and maintains project schedules.
- Risk Manager: Identifies and mitigates project risks.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates Agile project development processes.
A Project Manager often starts as a project coordinator or scheduler. As they gain experience, they move into senior roles. Certification like PMP (Project Management Professional) can enhance their career prospects.
Career Opportunities In Business Management
Business management careers involve overseeing the operations of a company. Professionals in this field focus on strategic planning, organizational leadership, and resource management.
- Business Manager: Manages daily operations and business strategies.
- Operations Manager: Oversees production and operational efficiency.
- Human Resources Manager: Manages employee relations and recruitment.
- Marketing Manager: Develops marketing strategies to promote products.
- Financial Manager: Manages the financial health of the organization.
A Business Manager might start in roles like operations or marketing. With experience, they can move into executive positions. An MBA (Master of Business Administration) is often beneficial for advancing in business management.
| Project Management | Business Management |
|---|---|
| Project Manager | Business Manager |
| Project Coordinator | Operations Manager |
| Project Scheduler | Human Resources Manager |
| Risk Manager | Marketing Manager |
| Scrum Master | Financial Manager |

Credit: pmstudycircle.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Project Management?
Project management involves planning, executing, and overseeing specific projects. It focuses on meeting goals within a set timeframe and budget.
What Is Business Management?
Business management covers managing an entire organization. It includes planning, organizing, leading, and controlling all business activities to achieve long-term objectives.
How Do Roles Differ In Project Vs. Business Management?
Project managers focus on specific project goals. Business managers oversee the overall business strategy and operations.
Which Is More Strategic: Project Or Business Management?
Business management is more strategic as it involves long-term planning and overall organizational goals. Project management is typically more tactical.
Conclusion
Project management focuses on specific projects and their completion. Business management oversees the overall operations of a company. Both roles are essential for success. Understanding their differences helps in better decision-making. Choose the right approach for your needs. Effective management leads to achieving goals and growth.